How To Find Density With Weight And Length Volume is the amount of space an object occupies while density is the mass of an object per unit volume. You need to know the volume of an object before you can calculate its density. Calculating volume for regular objects can be done with a simple formula determined by the shape of the object. Common units for volume are cubic centimeters , cubic meters , cubic inches , and cubic feet .
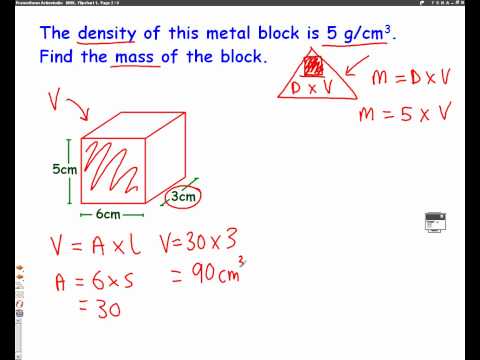
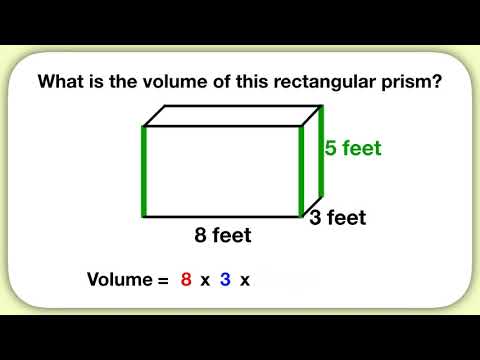
Once you have the volume, density is one more simple calculation away. Common units for density are grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) or grams per milliliter (g/mL). If the object is regular, you can use a volume formula. For example, the volume of a rectangular prism equals width x height x length. To make this calculation, measure the width, height and length of the object in centimeters. You can also use a graduated cylinder to measure volume.
Simply fill the graduated cylinder with water and note this measurement. Find the difference between the new and original measurements on the graduated cylinder. For your density calculation, you will need a volume in cubic centimeters, so convert units accordingly. Before you calculate density, calculate volume using the object's volume formula. For example, for a rectangular prism, measure its length, width, and height, then solve for volume using the formula where volume equals length × width × height.
After you have your object's volume, determine its mass by weighing it on a scale or with a balance. You can then calculate density by dividing the mass by the volume. For this lab, we will calculate the density of two cubes and a cylinder. For the two cubes, we will first measure the length, width, and height, in centimeters, of each cube using the vernier caliper. For the cylinder, we will measure the height and diameter, in centimeters, using the vernier caliper.
Next, using the digital mass balance, we will find the mass of each object in grams. Using these measurements, we will then calculate the densities of the objects, research the accepted densities of the objects, and then calculate our percent error on our calculation. In addition, we will calculate the percent uncertainties for the length, width, height, mass and density of each object.
If the values is in cubic inches, divide the number by 1,728 cubic inches, and answer will provide your cubic dimension. As mentioned above, dividing the weight by cubic dimension will provide the density. If the value is in cubic inches, divide the number by 1,728 cubic inches, then divide the weight by this number. Now that you have determined the shape, which formula to use, and made the necessary measurements, you can calculate volume. By plugging in the values of your measurements and doing the math.
Your finished product is the volume of your object.Remember to express your answer in cubic units. Whether you are using metric or SI, the unit of volume will always be cubic. Be sure to always add units to the end of your calculation.
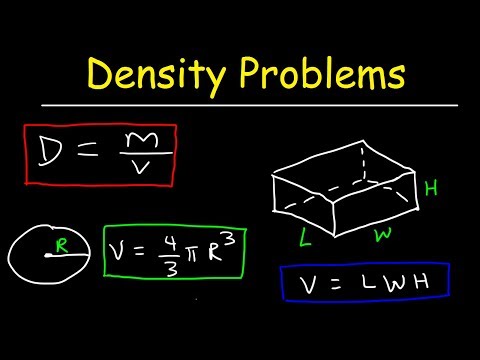
Our density calculator helps you determine your freight rate. When shipping LTL freight, you must know how to handle shipment density conversions to properly describe your goods on the bill of lading. Divide the total weight of a shipment by the total cubic feet to determine the density. Ρ is the object's density m is the object's total mass V is the object's total volume Under specified conditions of temperature and pressure, the density of a fluid is defined as described above.
However, the density of a solid material can be defined in several ways. Porous or granular materials have a density of the solid material, as well as a bulk density, which can be variable. For example, if you gently fill a container with sand, and divide the mass of sand by the container volume you get a value termed loose bulk density.
If you took this same container and tapped on it repeatedly, allowing the sand to settle and pack together, and then calculate the results, you get a value termed tapped or packed bulk density. Tapped bulk density is always greater than or equal to loose bulk density. In both types of bulk density, some of the volume is taken up by the spaces between the grains of sand. The density of the sand grains, exclusive of the air between the grains, will be higher than the bulk density.
Freight density is the measurement of the shipment's compactness or pounds per cubic foot . You will need to know your freight density when using a density-based carrier or when the NMFC for your shipment is Not Otherwise Indicated . Our freight density calculator will help you determine your cargo's density and freight class in seconds. Calculate the volume of the object using displacement. Measuring dimensions of objects that are irregularly shaped can be difficult and lead to inaccurate measurements and calculations of volume.
By measuring the amount of water displaced by an object, you can easily determine its volume without complex formulas. The density of a substance can be used to define the substance.Water is unusual because when water freezes, its solid form is less dense than liquid water, and thus floats on top of liquid water. In other words, the more space your freight occupies on a truck or in a container the more costs you will incur for transport. If your commodity or product cannot be classified by a National Motor Freight Classification number, than apply a general class rate or NOI class to determine your cost to ship.
NOI shipping terms are typically quoted and processed manually through select freight carriers. For this reason, shippers are encouraged to make sure their weights and dimensions are accurate in order to avoid billing adjustments based on PCF and class changes. By far the most common reason for a re-bill or billing adjustment, it is also the most avoidable.
Never guess or estimate dimensions and weights when shipping freight. Why do we need to calculate your shipment's density? A shipment's density is one of the factors that determines the freight rate. We need to know how to calculate a shipment's density so we can properly describe their goods on the bill of lading. To determine shipment density, we take the total weight of the shipment and divide it by the total cubic feet.
In determining the density of a shipment, multiply the length, width and height in inches of your shipment and then divide the product by 1,728 to obtain the cubic feet of the shipment. Dividing the weight by the number of cubic feet produces the shipment's pounds per cubic foot. Of a substance is the ratio of the mass of a sample of the substance to its volume. The SI unit for density is the kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3). For many situations, however, this as an inconvenient unit, and we often use grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) for the densities of solids and liquids, and grams per liter (g/L) for gases. Although there are exceptions, most liquids and solids have densities that range from about 0.7 g/cm3 to 19 g/cm3 .
Table \(\PageIndex\) shows the densities of some common substances. Using a pan balance, determine and record the mass of an object in grams. Using a vernier caliper or ruler, measure the length, depth and width of the object in centimeters.
Multiply these three measurements to find the volume in cubic centimeters. Divide the object's mass by its volume to determine its density. You can tell it is heavy enough to sink in water, but you can't use a ruler to measure its dimensions. To measure the toy's volume, fill a graduated cylinder about half way with water. Make sure to displace any air bubbles that may stick to it. The volume of the toy soldier is the final volume minus the initial volume.
You can measure the mass of the toy and then calculate density. The fastest way to find the density of an object is of course to use our density calculator. To make the calculation, you'll need to know a few other values to start with. After typing these values into the density calculator, it will give you the result in kilograms per cubic meter.
Density is equal to an object's mass divided by its volume. Note that to properly calculate density, you need to find the mass in grams. You can use a balance with gram weights, or you can find the mass with a scale and convert the units to grams.
Here is an example using a 42" x 48" x 48" skid weighing 500 pounds. Divide the weight of the shipment by the total cubic feet. The result is the pounds per cubic foot, i.e., density.
Because the density of water in g/cm3 is 1.0, the SG of an object is will be almost the same as its density in g/cm3. However, specific gravity is a unitless number, and is the same in the metric system or any other measurement system. It is very useful when comparing the density of two objects. Since specific gravity is unitless, it doesn't matter whether the density was measured in g/cm3 or in some other units (like lbs/ft3).
One of the many statements attributed to the Archimedes principle is that an object immersed in a fluid apparently loses weight by an amount equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. That principle makes it possible to determine of the density of a solid object that is denser than water and is so irregular in shape that its volume cannot be measured directly. The purpose of this lab is to calculate the different densities of three objects. To do this, we will use a vernier caliper and a digital mass balance. In addition, we will then calculate the percent error of our measurements. MetalProject the image MetalMost common metals like aluminum, copper, and iron are more dense than plastic or wood.
The atoms that make up metals are generally heavier than the atoms in plastic and wood and they are packed closer together. Plastics are made from individual molecules bonded together into long chains called polymers. These polymer chains are arranged and packed together to make the plastic.
One common plastic, polyethylene, is made up of many individual molecules called ethylene which bonded together to make the long polymer chains. Like most plastics, the polymers in polyethylene are made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. The carbon and hydrogen atoms are very light, which helps give plastics their relatively low density.
Plastics can have different densities because different atoms can be attached to the carbon-hydrogen chains. The density of different plastics also depends on the closeness of packing of these polymer chains. WoodProject the image WoodWood is made mostly from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together into a molecule called glucose.
These glucose molecules are bonded together to form long chains called cellulose. Many cellulose molecules stacked together give wood its structure and density.In general, the density of wood and plastic are similar because they are made of similar atoms arranged in long chains. The difference in density is mostly based on the arrangement and packing of the polymer chains. Also, since wood is from a living thing, its density is affected by the structure of plant cells and other substances that make up wood. Student groups will not need to measure the volume of the cubes.
The volume of each cube is the same, 15.6 cm3, and is given in their chart on the activity sheet. They will need to measure the mass of each of the eight different cubes and calculate their densities. Students will use their values for density to identify each cube. How can two objects, which are exactly the same size and shape, have a different mass? Help students understand that the difference in mass must have something to do with the atoms in each cube. There are three possible explanations about the copper and aluminum atoms in the cubes that could explain the difference in mass.
Copper atoms might have more mass than aluminum atoms. Students will be able to calculate the density of different cubes and use these values to identify the substance each cube is made of. Students will be able to explain that the size, mass, and arrangement of the atoms or molecules of a substance determines its density. Students will observe a copper and an aluminum cube of the same volume placed on a balance.
Students will try to develop an explanation, on the molecular level, for how this can be. Students are then given cubes of different materials that all have the same volume. Students determine the density of each cube and identify the substance the cube is made from.
The most accurate way to calculate the density of any solid, liquid or gas is to divide its mass in kilograms by its volume (length × width × height) in cubic metres. Length 48", Width 40", Height 28" (20" plus 8" of pallet) equals 53,760 cubic inches or 31.1 cubic feet. Point out that the copper atoms are slightly smaller than aluminum atoms. This smaller size means that more copper atoms can fit in the same amount of space.